What Is Layer 2?
Blockchain technology, the backbone of cryptocurrencies, has revolutionized the way we think about transactions and data security. At its core, blockchain operates on a decentralized and transparent ledger system. However, as the popularity of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum soared, scalability issues have emerged, giving rise to Layer 2 blockchains–the innovative answer to scaling challenges.
This article breaks down the big concept behind Layer 2s and how they work, so that you can do clear-headed research the next time you’re thinking about investing in any Layer 2 blockchain.
What is a Layer 2 Blockchain?
Before delving into Layer 2 solutions, let's grasp the concept of blockchain layers. In the blockchain realm, the term "layers" refers to different levels or protocols that contribute to the overall functionality of the system.
Layer 1, the base layer, is where the primary blockchain network operates. Bitcoin and Ethereum are notable examples of Layer 1 blockchains. These networks are fundamental, but as transaction volumes increase, scalability becomes a bottleneck.
Layer 2 solutions act as a supplementary layer built on top of existing blockchains, enhancing their efficiency and scalability. Think of it like adding an express lane to a busy highway – faster, more efficient, and designed to reduce congestion.
How do Layer 2s Work?
Let’s see how Layer 2s work, step-by-step (without getting too technical!), using this same transportation analogy:
- Base layer: Imagine the base layer of a blockchain (Layer 1) as the main highway where all transactions happen. It's like the primary road for all cars (transactions) in the city.
- Layer 2 introduction: Now, as more people start using the road, it gets congested, and transactions become slower and more expensive. Here's where Layer 2 solutions come in. They're like adding a fast, extra lane to the road, specifically for smaller and quicker transactions.
- Off-chain processing: Layer 2 solutions work by moving a lot of the smaller transactions "off-chain." Think of it as having a local coffee shop where people can quickly exchange small amounts without clogging up the main road.
- State channels and payment channels: One common type of Layer 2 solution is called a "state channel" or "payment channel." It's like opening a tab at a bar. Instead of recording every drink purchase on the main road, you open a tab (state channel) and settle the final bill on the main road when you're done.
- Reduced main chain load: By conducting most of these quick transactions off the main road, Layer 2 solutions reduce the traffic on the main blockchain. This not only speeds things up but also makes it more cost-effective, like taking smaller transactions off the main toll road.
- Final settlement on main chain: Once the tab is closed or the state channel reaches a certain point, the final result is settled on the main blockchain. It's like closing the tab at the bar and updating the main road with the total number of drinks consumed.
Examples of Layer 2 Solutions
Bitcoin's Lightning Network:
The Lightning Network is like a high-speed rail system for Bitcoin transactions. Picture the base layer (Layer 1) as the main railway track, and the Lightning Network as a network of interconnected bullet trains running parallel. This off-chain scaling solution enables faster and cheaper transactions by conducting most microtransactions off the main blockchain, settling only the final result on the Bitcoin network.
Ethereum's Rollups:
Ethereum, facing scalability challenges due to its popularity, has embraced Layer 2 solutions like Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups. Imagine Ethereum as a bustling city with Rollups acting as efficient metro systems. Instead of everyone crowding the main roads (Layer 1), transactions are processed faster and at a lower cost within the metro system (Rollups), with occasional check-ins on the main roads for security.
Layer 2 Blockchains vs Sidechains
While both sidechains and Layer 2 solutions aim to address scalability issues in blockchain networks, they are distinct concepts with different approaches to achieving this goal. Let's compare them side-by-side to gain a high-level overview of their differences:
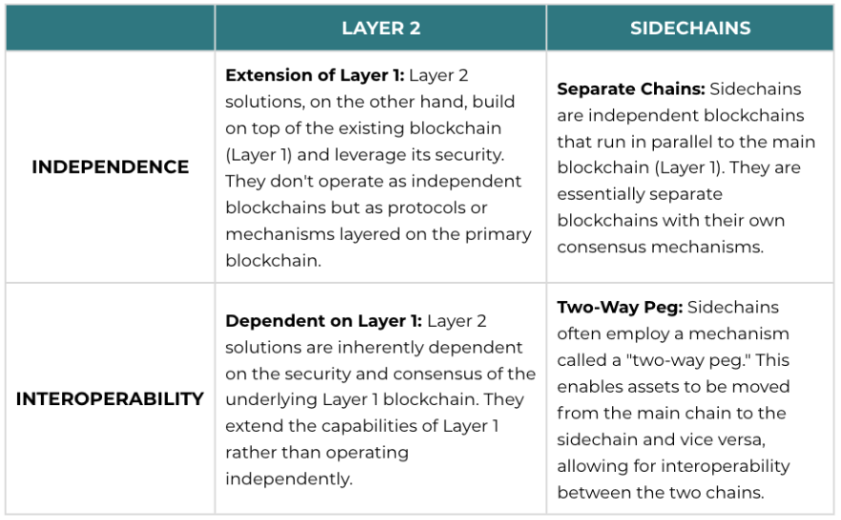
In summary, sidechains and Layer 2 solutions are both strategies to enhance blockchain scalability, but they differ in their independence, consensus mechanisms, and interoperability approaches. Understanding these distinctions is essential when exploring how different projects address the challenges of blockchain scalability.
How Layer 2 Solutions Shape the Blockchain Industry
- Scalability: Layer 2 solutions address the scalability problem that haunts many Layer 1 blockchains. By moving a significant portion of transactions off-chain, these solutions increase the overall network capacity, ensuring smoother and faster transactions.
- Cost-efficiency: The off-chain nature of Layer 2 transactions often results in lower fees, making microtransactions economically viable. This opens up new possibilities, especially in scenarios where small transactions were previously impractical due to high fees on the main blockchain.
- Enhanced user experience: Faster transaction speeds and reduced costs contribute to a more user-friendly experience. This is crucial for the mass adoption of blockchain technology, as users expect transactions to be as seamless and quick as traditional payment methods.
Challenges Facing Layer 2 Solutions
While Layer 2 solutions bring significant advantages to the blockchain ecosystem and do help address blockchain scalability issues to a certain degree, they also face several challenges, such as:
- Interoperability: Achieving interoperability between different Layer 2 solutions and even between Layer 2 and Layer 1 can be a complex task. Seamless communication and data transfer between these layers are essential for a cohesive and efficient blockchain ecosystem. Without robust interoperability standards, users might face difficulties in moving assets and data across different layers.
- Security concerns: Layer 2 solutions introduce additional complexity to the overall security model of a blockchain. While they often leverage the security of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain, vulnerabilities specific to Layer 2 can emerge. Smart contract bugs, implementation flaws, or attacks targeting the off-chain components can pose significant security risks. Robust security measures are essential to maintain the integrity of Layer 2 solutions.
- Decentralization trade-offs: Some Layer 2 solutions may involve trade-offs in terms of decentralization. For example, solutions relying heavily on trusted entities or operators might introduce central points of control leading to single points of failure, deviating from the decentralized ethos of blockchain technology. Striking the right balance between scalability and decentralization remains a challenge for Layer 2 developers.
- Liquidity challenges: Some Layer 2 solutions, particularly those involving sidechains, may face liquidity challenges. If assets are thinly traded on Layer 2 or if there's insufficient liquidity to facilitate large transactions, it could impact the efficiency and effectiveness of these solutions.
Addressing these challenges will be essential for the continued success and widespread adoption of Layer 2 solutions. Overcoming these hurdles requires collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to refining and optimizing the technologies that enhance the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Layer 2 solutions are pivotal in reshaping the blockchain landscape, providing solutions to the scalability challenges faced by Layer 1 blockchains in order to create more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable blockchain networks. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of Layer 2 solutions will likely play a crucial role in bringing blockchain technology closer to mainstream adoption.
Trade popular Layer 2 tokens and more on CoinW
You May Also Like
Stablecoin Divergence: USDC vs. USDT
In the world of digital assets, if Bitcoin is digital gold and Ethereum is the global computer, then stablecoins are the "main highways" and "settlement ports" connecting the real-world financial system with the crypto economy.

Altcoin Trading: From Entry to Advanced
In the world of cryptocurrency, if Bitcoin is digital gold and the anchor of the entire market, then Altcoins are the most active, imaginative, and challenging frontier within this ecosystem.

A Comprehensive Guide to DeFi’s Architecture, Yield Mechanisms, and Narrative Evolution
DeFi: Reconstructing finance with code, empowering every individual to be their own bank.
